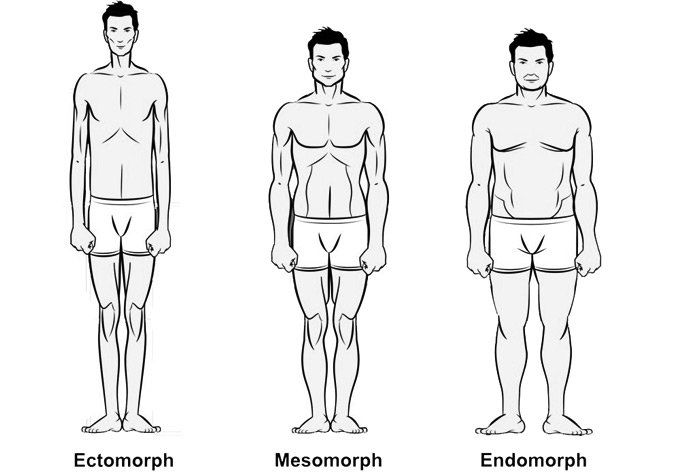
Understanding male body types is essential for making informed decisions about fitness, fashion, and overall health. Your body type—whether ectomorph, mesomorph, or endomorph—plays a crucial role in how you gain muscle, store fat, and respond to different training styles. Genetics largely determine your physique, but lifestyle choices, exercise, and diet can help you optimize your body composition.
This guide will help you identify your body type and provide practical tips on workouts, diet, and fashion choices to enhance your lifestyle. Whether you're looking to build muscle, lose weight, or dress in a way that complements your physique, recognizing your body type is the first step toward achieving your goals.
The Three Main Male Body Types
1. Ectomorph (Lean and Skinny)
Ectomorphs are naturally slim and often struggle to gain weight or muscle due to their fast metabolism. They have a light bone structure and long limbs, making them appear tall and slender.
Characteristics:
-
Naturally slim with a small bone structure and narrow shoulders
-
Long limbs (arms and legs), making them appear taller and leaner
-
Fast metabolism, which makes it hard to gain both muscle and fat
-
Thin wrists and ankles
-
Flat chest and lower muscle mass compared to other body types
Best Workout Strategies for Ectomorph:
To gain muscle and strength, ectomorphs should focus on progressive overload (gradually increasing weights and intensity).
Strength Training: Prioritize Compound Movements Like:
-
Kettlebell Goblet Squats – A great way to build lower-body strength while improving mobility and core engagement. Maintaining proper squat technique is essential for optimizing performance and preventing injuries.
-
Kettlebell Deadlifts – Build real strength from the ground up by developing stability, mobility, and power. Kettlebell deadlifts fire up your posterior chain and grip, making every rep count toward functional power.
-
Kettlebell Rows & Pull-ups – Maximize your upper-body strength and posture with kettlebell rows and pull-ups. Explore different variations to challenge yourself and keep progressing.
-
Kettlebell Floor Press – The floor press is a stable exercise that reduces shoulder strain while strengthening the chest and triceps.
Reps & Sets: 6–10 reps per set, with heavy weights and longer rest periods (1.5–2 minutes)
Limit cardio: Excessive cardio burns too many calories and makes muscle gain harder. Stick to low-intensity cardio 2–3 times a week for overall health.
2. Mesomorph (Athletic and Muscular)
Mesomorphs have a naturally muscular and athletic build, making it easier for them to gain muscle and lose fat. They have a well-proportioned body with broad shoulders, a narrow waist, and an overall balanced physique.
Characteristics:
-
Naturally muscular with a well-balanced frame
-
Medium-sized bone structure with broad shoulders and a narrow waist
-
Gains muscle easily and loses fat with minimal effort
-
Generally strong and athletic even without intense training
-
Responds well to both strength training and cardio
Best Workout Strategies for Mesomorph:
Mesomorphs have a natural advantage when it comes to fitness. Their bodies respond well to both strength training and cardio.
Balanced training routine: Combine strength training with functional exercises and moderate cardio
Strength training focus:
-
Compound lifts like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses for strength
-
Isolation exercises (bicep curls, leg extensions) to define muscles
-
Mix heavy and moderate weights (8–12 reps per set)
3. Endomorph (Stocky and Round)
Endomorphs have a larger and softer body structure, making them more prone to gaining fat. They often have a slower metabolism and need to work harder to stay lean. However, they also have a strong ability to gain muscle.
Characteristics:
-
Naturally bigger, rounder, and stockier than other body types
-
Broad shoulders but often carries more body fat
-
Thicker bone structure and shorter limbs
-
Slower metabolism, making it easier to gain weight but harder to lose fat
-
Strong muscle-building potential, but fat loss requires extra effort
Best Workout Strategies for Endomorphs:
Endomorphs need a combination of strength training and cardio to build muscle while burning fat.
Strength training focus:
-
Heavy lifting with higher reps (10–15 reps per set)
-
Incorporate full-body workouts to keep metabolism high
-
Use supersets (two exercises back-to-back) to maximize calorie burn
Hybrid Body Types (Combination Types)
Most people don’t fit neatly into the classic Ectomorph, Mesomorph, or Endomorph categories. Instead, they exhibit traits from multiple body types, forming hybrid body types like Ecto-Mesomorphs and Meso-Endomorphs. These hybrid types influence muscle-building potential, fat storage tendencies, metabolism speed, and overall physique development.
-
Ecto-Meso (Ectomorph-Mesomorph Hybrid) – A body type that combines characteristics of an ectomorph (naturally lean, fast metabolism) and a mesomorph (naturally muscular, athletic build). Individuals with this body type have a lean frame but can build muscle moderately with proper training and nutrition. They do not gain fat easily and tend to have a toned, athletic appearance rather than a bulky one.
-
Meso-Endo (Mesomorph-Endomorph Hybrid) – A body type that blends traits of a mesomorph (muscular, strong, naturally athletic) and an endomorph (broad, softer, stores fat easily). These individuals are naturally muscular but have a slower metabolism, meaning they gain fat easily if their diet and exercise are not well-managed. They have a powerful, stocky build and can develop a bulky physique if body fat is not controlled.
The Five Types of Male Body Shapes
Rectangle (Straight Body Shape)
The rectangle body shape has a balanced structure where the shoulders, waist, and hips are almost equal in width. This creates a straight silhouette with minimal curves. Individuals with this shape often have a naturally lean frame and may struggle to create definition in their waistline.
-
Shoulders, waist, and hips are nearly the same width, creating a straight vertical frame
-
Typically tall and lean with long limbs
-
Flat chest and narrow shoulders, leading to a less defined upper body
-
Minimal curves and muscle definition
Styling Tips:
-
Wear structured clothing (jackets, blazers) to create the illusion of broader shoulders
-
Layer outfits (sweaters, vests) to add visual weight
-
Horizontal stripes and bold patterns can help add width to your frame
-
Avoid baggy clothing, as it may make you look even thinner
Triangle (Pear Shape)
The triangle body shape has wider hips than shoulders, giving the lower body a more prominent appearance. This shape often comes with a defined waist and a naturally feminine silhouette. The goal is to balance proportions by enhancing the upper body.
-
Hips and waist are wider than the shoulders, creating a bottom-heavy appearance
-
Fat accumulation around the lower belly, hips, and thighs
-
Often found in endomorphs (those prone to fat gain)
Styling Tips:
-
Dark-colored pants and lighter tops help balance proportions
-
Wear structured blazers and jackets to broaden the upper body
-
Avoid skin-tight shirts, as they highlight a wider midsection
-
Slim, straight-leg trousers work better than baggy or skinny fits
Inverted Triangle
This body shape features broad shoulders with a narrower waist and hips, creating a top-heavy appearance. It is common among athletic individuals with a naturally strong upper body. The goal is to soften the shoulders and add volume to the lower body.
-
Broad shoulders and chest with a narrow waist and hips
-
Often found in athletic and muscular men (common in mesomorphs)
-
Strong, muscular upper body with low body fat
-
Seen in swimmers, gymnasts, and bodybuilders
Styling Tips:
-
Wear V-neck shirts to highlight the natural V-taper of the body
-
Choose fitted clothing, but avoid ultra-tight shirts that emphasize the upper body too much
-
Opt for straight-leg or slightly relaxed pants to balance proportions
-
Avoid skinny jeans, as they can make the upper body look too big
Oval (Round Shape)
The oval body shape is characterized by a fuller midsection with a rounder frame. Weight is often carried around the waist, while the arms and legs may appear slimmer. The goal is to elongate the body and create a structured look.
-
Weight is carried around the midsection, creating a rounded belly
-
Shoulders and chest may be narrower than the waist
-
Fat accumulates around the stomach, chest, and face
-
Typically seen in overweight or older men
Styling Tips:
-
Wear vertical stripes to create a slimming effect
-
Opt for dark colors and structured clothing to add definition
-
Avoid tight clothes that highlight the midsection
-
Choose V-neck shirts to draw attention upward
Trapezoid (Athletic Build)
The trapezoid body shape is naturally well-proportioned, with broad shoulders and a slightly narrower waist. This balanced frame is easy to style, as most clothing fits well. The goal is to enhance natural proportions without adding bulk.
-
Well-proportioned shoulders, chest, and waist
-
Often associated with mesomorphs (naturally athletic body types)
-
Broad shoulders, defined chest, and a slightly tapered waist
-
Seen in most fit and athletic men
Styling Tips:
-
Well-fitting clothes look great on this body type
-
Highlight the natural shape with fitted shirts and tapered trousers
-
Experiment with different styles, as most will suit this shape
How to Identify Your Body Type
Understanding your body type is essential for optimizing your fitness routine, diet, and even clothing choices. Most people do not fit into a single body type but rather a combination of two. Below is a step-by-step guide to determining your body type.
Step 1: Understand the Three Primary Body Types
-
Ectomorph (Lean and Slim)
-
Mesomorph (Athletic and Muscular)
-
Endomorph (Broad and Soft)
Step 2: Analyze Your Body Structure
A. Bone Structure (Wrist and Ankle Test)
A quick way to assess your frame is by measuring your wrist size:
-
Wrap your thumb and middle finger around your opposite wrist.
-
If they overlap significantly → Likely an ectomorph
-
If they just touch → Likely a mesomorph
-
If they don’t touch → Likely an endomorph
B. Shoulder-to-Waist Ratio
-
Ectomorphs – Shoulders and waist are close in width; little natural V-taper.
-
Mesomorphs – Broad shoulders, narrower waist, forming a natural V-shape.
-
Endomorphs – Shoulders and waist tend to be similar in width, with a softer midsection.
Step 3: Assess Your Muscle and Fat Distribution
-
How Easily Do You Gain Muscle?
-
Hard to gain muscle? → Likely an ectomorph
-
Gain muscle easily? → Likely a mesomorph
-
Gain muscle but also store fat easily? → Likely a meso-endomorph
-
How Easily Do You Gain Fat?
-
Struggle to gain weight even with a high-calorie diet? → Ectomorph
-
Can gain fat but also lose it with effort? → Mesomorph
-
Gain fat easily and find it harder to lose? → Endomorph
Step 4: Observe Your Metabolism
-
Fast metabolism? You stay lean no matter what you eat → Ectomorph
-
Moderate metabolism? You can gain or lose weight relatively easily → Mesomorph
-
Slow metabolism? You gain weight easily and need to be strict with diet → Endomorph
Step 5: Compare Your Findings to Hybrid Body Types
If you show characteristics of multiple types, you may have a hybrid body type:
-
Ecto-Mesomorph → Naturally lean with some ability to build muscle.
-
Meso-Endomorph → Muscular but gains fat easily.
-
Ecto-Endomorph → A rare type where a person is slim in some areas but stores fat in specific regions.
Step 6: Track How Your Body Responds to Training
A great way to confirm your body type is by observing how you react to different workout styles:
-
Ectomorphs should focus on strength training with minimal cardio to build muscle.
-
Mesomorphs can train with a mix of weights and cardio to maintain a lean, muscular physique.
-
Endomorphs should prioritize fat-burning workouts and diet control to avoid excessive weight gain.
Hybrid Body Types (Combination Types)
Most people don’t fit neatly into the classic Ectomorph, Mesomorph, or Endomorph categories. Instead, they exhibit traits from multiple body types, forming hybrid body types like Ecto-Mesomorphs and Meso-Endomorphs. These hybrid types influence muscle-building potential, fat storage tendencies, metabolism speed, and overall physique development.
-
Ecto-Meso (Ectomorph-Mesomorph Hybrid) – A body type that combines characteristics of an ectomorph (naturally lean, fast metabolism) and a mesomorph (naturally muscular, athletic build). Individuals with this body type have a lean frame but can build muscle moderately with proper training and nutrition. They do not gain fat easily and tend to have a toned, athletic appearance rather than a bulky one.
-
Meso-Endo (Mesomorph-Endomorph Hybrid) – A body type that blends traits of a mesomorph (muscular, strong, naturally athletic) and an endomorph (broad, softer, stores fat easily). These individuals are naturally muscular but have a slower metabolism, meaning they gain fat easily if their diet and exercise are not well-managed. They have a powerful, stocky build and can develop a bulky physique if body fat is not controlled.
How to Improve Your Body Type with Fitness & Nutrition
Fitness Plan for Ectomorphs
Since ectomorphs struggle to gain muscle and strength, they should focus on:
Heavy weightlifting – Prioritize compound exercises like squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and rows.
Low reps, heavy weight – 4–6 reps per set with heavier weights for muscle growth.
Less cardio – Too much cardio burns calories that could be used for muscle gain.
Workout frequency – Train each muscle group at least 2 times per week.
Nutrition Plan for Ectomorphs
High-calorie diet – Eat more than you burn to gain muscle.
High protein intake – Aim for 1.2–1.5g of protein per pound of body weight
Healthy carbs – Include whole grains, oats, rice, potatoes, and fruits.
Healthy fats – Add nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil to boost calories.
Fitness Plan for Mesomorphs
Since mesomorphs gain muscle easily, they should focus on:
Strength training + moderate cardio – A mix of weightlifting and 2-3 days of cardio per week.
Balanced rep ranges – 8–12 reps per set for muscle definition and endurance.
High-intensity workouts – Supersets and circuit training help maintain a lean, muscular physique.
Progressive overload – Continually increase weights and intensity to keep making gains.
Nutrition Plan for Mesomorphs
Balanced macros – A mix of protein, carbs, and fats to support muscle maintenance.
Moderate calorie intake – Eat according to your goals (bulk, maintain, or cut).
Protein-rich meals – Ensure 1–1.2g of protein per pound of body weight for muscle maintenance.
Quality carbs – Choose brown rice, quinoa, sweet potatoes, and whole grains.
Hydration – Drink plenty of water to support metabolism and muscle recovery.
Fitness Plan for Endomorphs
Endomorphs tend to store fat easily, so they should focus on:
High-intensity cardio – HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training) 3–4 times per week for fat burning.
Strength training – Full-body workouts with compound movements to build muscle and boost metabolism.
Higher reps, moderate weight – 12–15 reps per set to maximize fat loss.
Active lifestyle – Include walking, cycling, or swimming to keep burning calories throughout the day.
Nutrition Plan for Endomorphs
Caloric deficit – Consume fewer calories than you burn to promote fat loss.
Low-carb diet – Reduce refined carbs and sugars, focusing on lean proteins and healthy fats.
High-protein intake – Aim for 1.2–1.5g of protein per pound of body weight to preserve muscle.
Fiber-rich foods – Vegetables, legumes, and whole grains help with digestion and satiety.
Meal timing – Eat smaller, frequent meals to stabilize blood sugar levels and avoid fat storage.
FAQ Questions?
1: What Type of Male Body is Most Attractive?
According to National library of medicine, the most attractive male body type is an inverted triangle shape, characterized by broad shoulders and a narrow waist. This physique signifies strength and muscle development, often perceived as masculine and attractive
2. Which Body Type is Hardest to Gain Muscle?
Ectomorphs find it hardest to gain muscle due to a fast metabolism. They don’t necessarily have low testosterone but may struggle with muscle growth. An attractive waist size is around 30-34 inches, and the mesomorphic body type is often considered ideal for strength and aesthetics.
3. Do Ectomorphs Have Low Testosterone?
According to Medical News Today, Ectomorphs don’t necessarily have low testosterone but may struggle with muscle gain. An attractive waist size for men is around 30-34 inches, and the mesomorphic body type is often considered ideal.
4: Which Body Type is Best for Males?
According to MedicineNet, The mesomorphic body type is often considered the best for males due to its balanced muscle mass, strength, and athletic build. It allows for easier muscle gain, fat loss, and overall physical performance.
5: What is the Attractive Waist Size for a Man?
An attractive waist size for a man is typically around 30-34 inches, as it creates a V-shaped torso with broad shoulders. This proportion is often associated with strength, fitness, and masculinity.
References
Somatotypes (Ectomorph, Mesomorph, Endomorph) -
Sheldon, W. H. (1940). The Varieties of Human Physique: An Introduction to Constitutional Psychology. Harper & Brothers.
General Information Link (Mayo Clinic): https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/adult-health/expert-answers/body-types/faq-20058286
Workout Strategies for Ectomorphs (Strength Training, Compound Movements, Limiting Cardio):
Link (ACSM - Strength Training Guidelines): https://www.acsm.org/education-resources/trending-topics/strength-training
Workout Strategies for Endomorphs (Strength Training, High Reps, Full Body Workouts, Supersets):
Link (HIIT Training - ACE Fitness): https://www.acefitness.org/resources/everyone/blog/6407/6-things-to-know-about-high-intensity-interval-training/
Male Body Shapes (Rectangle, Triangle, Inverted Triangle, Oval, Trapezoid):
Link (Example Men's Style Guide - Real Men Real Style): https://www.realmenrealstyle.com/
Fitness & Nutrition Plans for Each Body Type (General Advice):
Link (NIH - Healthy Eating): https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/education/healthy-eating