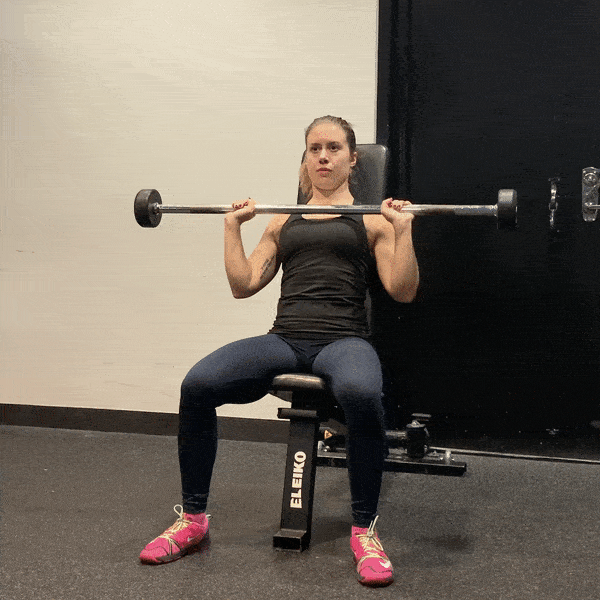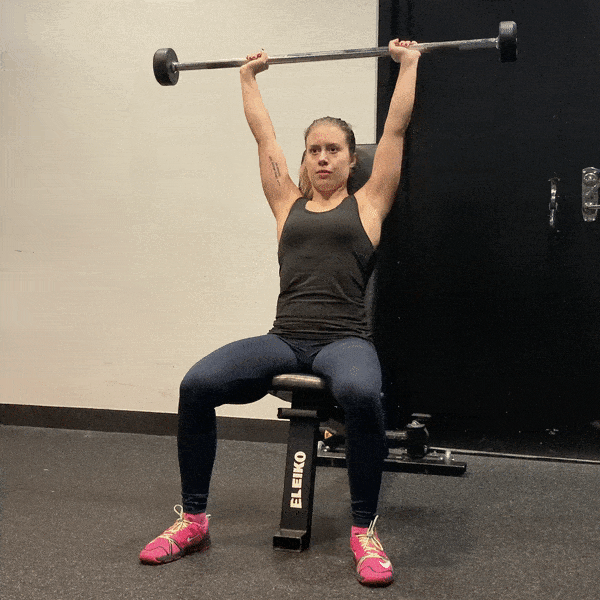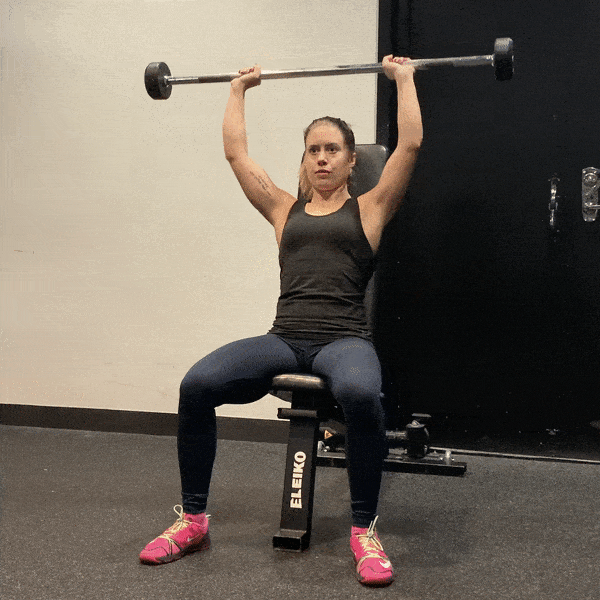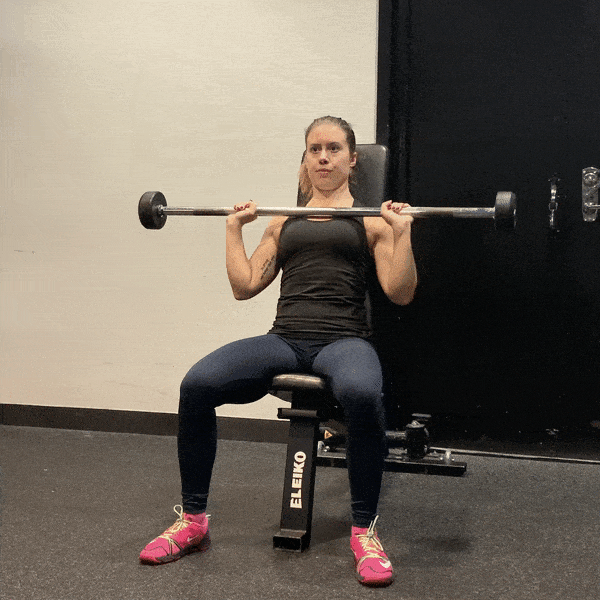Back workouts are essential for women seeking to enhance their strength, improve posture, and achieve a balanced physique. Many women often overlook back training, focusing more on the arms, legs, and core. However, neglecting back workouts can lead to muscle imbalances and postural issues, potentially causing discomfort and increasing the risk of injuries.
This article will explore the importance of back workouts, effective exercises, how often to train, tips for effective workouts, and expert advice on designing a back workout routine tailored for women.
Understanding Back Muscles Anatomy

Before we embark on the journey of back exercises, let's explore the intricate anatomy of the back. The major muscle groups include the latissimus dorsi (lats), rhomboids, traps, erector spinae, and more. Balanced development of these muscles is not only aesthetically pleasing but also essential for maintaining proper posture and supporting daily movements.
Latissimus Dorsi (Lats):The lats are large, fan-shaped muscles that drive movements like pulling, helping with shoulder extension, adduction, and medial rotation.
Rhomboids: These are Located between the shoulder blades, rhomboids support scapulae retraction, crucial for maintaining proper posture.
Trapezius: The trapezius is an extensive muscle supporting the upper spine and assisting in various shoulder movements, contributing to shoulder stability.
Erector Spinae: Running along the spine, erector spinae muscles play a crucial role in spinal extension, impacting upright posture.
Terres Major and Minor, Infraspinatus, Supraspinatus: These muscles assist in shoulder movement and stability, contributing to overall shoulder joint health.
Understanding these muscles provides insight into their specific functions, aiding in targeted workouts and overall back health.
Importance of Back Workouts for Women
Improved Posture and Pain Relief
Strengthening back muscles plays a crucial role in improving posture and alleviating back pain. A strong back can counteract the effects of prolonged sitting or desk work, which can lead to slouched shoulders and rounded backs. Proper posture not only enhances appearance but also reduces the strain on spinal structures.
Enhanced Overall Strength and Functionality
The back is integral to overall body strength. Strong back muscles support functional movements such as lifting, reaching, and bending, making daily activities easier and safer.
Toned and Defined Back
Many women desire a toned back for aesthetic reasons. Well-developed back muscles contribute to a balanced physique, enhancing the appearance of the arms, shoulders, and waist.
Injury Prevention
A strong back supports the spine and helps prevent injuries during physical activities. Strengthening the back can mitigate the risk of common injuries associated with poor lifting techniques or sudden movements.
Support Daily Activities
A strong back is essential for performing everyday tasks, from carrying groceries to playing with children. Incorporating back workouts into your routine can improve quality of life and increase independence.
Incorporating Back Workouts into Your Routine
To harness the benefits of back workouts, women should incorporate a variety of exercises into their fitness routines at least twice a week. It’s essential to target different areas of the back, including the latissimus dorsi, rhomboids, trapezius, and erector spinae muscles. Here are some recommendations for integrating back workouts effectively:
- Frequency: Aim for back workouts 2-3 times per week. This allows for adequate recovery between sessions while promoting muscle growth and strength.
- Variety: Include a mix of compound exercises (which target multiple muscle groups) and isolation exercises (which focus on specific muscles) to ensure comprehensive training.
- Weight Selection: Start with lighter weights to master proper form before progressing to heavier loads. Prioritize form over weight to reduce the risk of injury.
How Often Women Should Do Back Workouts
The frequency of back workouts depends on individual fitness goals and overall programming. As a general guideline:
- For General Fitness and Toning: Include back exercises 2-3 times per week, allowing for proper recovery between sessions.
- For Strength and Muscle Building: Prioritize back workouts 2-3 times per week, with at least one day of rest between sessions to allow for recovery.
- For Advanced Lifters: Incorporate back exercises more frequently, sometimes splitting workouts into upper and lower back focus.
Best Back Exercises for Women
1. Alternating Renegade Row
This exercise targets the upper back and core.
- Setup: Start in a high plank position with a dumbbell in each hand, wrists directly under shoulders, and feet slightly wider than hip-width apart.
- Execution: Keeping your core engaged, lift one dumbbell towards your hip while balancing on the opposite arm. Lower it back down and alternate sides.
2. Bent-Over Row
A compound exercise for overall back strength.
- Setup: Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, holding a barbell or dumbbells in front of your thighs.
- Execution: Hinge forward at the hips, keeping your back flat. Pull the weight towards your lower ribcage, squeezing your shoulder blades together, then lower it back down.
3. Reverse Flye
This exercise isolates the rear deltoids and upper back.
- Setup: Stand with feet hip-width apart, holding dumbbells in front of your thighs.
- Execution: With a slight bend in your elbows, raise the dumbbells out to the sides until shoulder height, squeezing your shoulder blades together. Lower back down with control.
4. One-Arm Dumbbell Row
Focuses on the lats and rhomboids.
- Setup: Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, holding a dumbbell in one hand.
- Execution: Hinge forward at the hips and place the opposite hand on a bench for support. Pull the dumbbell towards your hip, retracting your shoulder blade. Lower it back down and switch sides.
5. Upright Row
This targets the upper traps and shoulders.
- Setup: Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, holding a barbell or dumbbells in front of your thighs.
- Execution: Pull the weights up towards your chin, leading with your elbows. Lower them back down under control.
6. Plank Up-Down
This exercise builds core and back strength.
- Setup: Start in a forearm plank position with elbows under shoulders.
- Execution: Push up onto one hand, then the other, transitioning to a high plank. Lower back down, alternating arms.
7. Overhead Press
A compound movement that strengthens the shoulders and upper back.
- Setup: Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, holding a barbell or dumbbells at shoulder height.
- Execution: Press the weight overhead until arms are fully extended, then lower back to shoulder height.
8. Bird Dog Exercise
This exercise enhances core stability and back strength.
9.Lat Pulldown
The lat pulldown is an essential exercise that primarily targets the latissimus dorsi muscles in the back, as well as the biceps and other upper back muscles. It's a great way to build upper body strength and improve posture.
- Setup: Sit on the lat pulldown machine with your knees secured under the leg pads. Adjust the thigh pad height for a snug fit and keep your feet flat on the floor.
- Execution: Grasp the wide bar or handles with an overhand grip, slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Pull the bar down smoothly towards your upper chest by primarily engaging your lats. Focus on pulling your elbows down and back, squeezing your shoulder blades together at the bottom of the movement. Allow the bar to return to the starting position with control and repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Tips for Effective Back Workouts for Women
- Warm-Up: Always start with a warm-up to prepare your muscles and joints. Dynamic stretches and light cardio can increase blood flow and reduce the risk of injury.
- Focus on Form: Prioritize proper form over lifting heavier weights. Incorrect form can lead to injuries and undermine the effectiveness of the workout.
- Mind-Muscle Connection: Concentrate on the muscles being worked during each exercise. This can enhance muscle activation and improve results.
- Incorporate Progressive Overload: Gradually increase the weights you use as your strength improves. This can stimulate muscle growth and prevent plateaus.
- Cool Down: End each session with stretching to improve flexibility and aid in recovery. Focus on the back, shoulders, and chest to promote balance.
Aligning Back Workouts with Women's Fitness Goals
Women's fitness goals can vary widely, from building strength and muscle to toning and improving functional fitness. Aligning back workouts with specific goals can optimize results and enhance overall fitness. Here's how back workouts can be tailored to support different fitness objectives for women:
- Strength and Muscle Building: To build strength and muscle mass in the back, focus on compound exercises that engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously. Use progressive overload by gradually increasing weights over time to challenge the muscles. Allow adequate recovery between workouts to promote muscle growth and adaptation.
- Toning and Definition: For toning and defining the back muscles, incorporate a higher volume of exercises with moderate weights and higher repetitions. This approach helps enhance muscle endurance and definition without significant muscle mass gain.
- Functional Fitness: Functional back exercises mimic real-life movements and improve overall functional fitness. Prioritize exercises that involve pulling, lifting, and stabilizing motions, which strengthen the back for everyday activities and sports performance.
- Posture and Injury Prevention: To improve posture and prevent injuries, target the erector spinae, trapezius, and rhomboid muscles. Strengthening these muscles helps stabilize the spine, correct postural imbalances, and reduce the risk of back-related injuries.
Preventing Common Back Injuries in Women
Back injuries can affect anyone, but certain factors make women particularly susceptible. Many women may experience weaker back muscles due to:
- Sedentary Lifestyles: Many women engage in jobs or daily routines that require prolonged sitting, leading to weakened back muscles. Over time, the lack of physical activity can result in muscular imbalances, where certain muscles become weak and others overly tight, increasing the risk of injury.
- Improper Lifting Techniques: In everyday life, women may lift heavy objects without proper form, which can lead to strain or injury. Common mistakes include bending at the waist instead of the knees, twisting the torso while lifting, and not engaging the core muscles.
To prevent these injuries, it is crucial to focus on exercises that strengthen both the back and core muscles. A strong core provides stability and support for the spine, reducing the likelihood of injuries. Here are some effective strategies for injury prevention:
- Strength Training: Incorporating exercises that target the back, such as rows, deadlifts, and pull-ups, can strengthen the muscles that support the spine. Strengthening the muscles around the back helps create a more stable structure that can better handle everyday stresses.
- Core Exercises: Strengthening the core muscles, including the abdominals, obliques, and lower back, provides essential support for the spine during movement. Planks, bridges, and pelvic tilts are excellent core exercises that contribute to back health.
- Flexibility Training: Stretching and flexibility exercises, such as yoga or Pilates, can improve muscle elasticity and reduce tension. Flexibility in the muscles surrounding the spine helps maintain a healthy range of motion and can prevent injuries from tightness.
- Proper Lifting Techniques: Learning and practicing correct lifting techniques—such as bending at the knees and keeping the load close to the body—can significantly reduce the risk of back injuries during daily activities.
Progression and Variation in Back Workouts for Women
Progression and variation are vital principles in any strength training program, including back workouts. They are essential for continued improvement, muscle growth, and preventing plateaus. Here’s how these principles apply to back training for women:
-
Progressive Overload
This principle involves gradually increasing the weight or resistance used in exercises over time. For women, this could mean lifting heavier weights, increasing the number of sets or repetitions, or shortening rest periods between sets. Progressive overload ensures that muscles continue to be challenged, which is crucial for growth and strength development.
-
Changing Exercise Angles
Modifying the angles at which exercises are performed can engage different muscle fibers and promote balanced muscle development. For example, performing bent-over rows with different grips (overhand vs. underhand) or changing the incline of a bench can target the back muscles differently.
-
Incorporating New Movements
Regularly introducing new exercises into the workout routine keeps training fresh and exciting while also preventing adaptation. This could involve trying different variations of traditional exercises, such as kettlebell swings, inverted rows, or cable exercises.
-
Adjusting Volume and Intensity
Women can adjust the volume (the total number of sets and reps) and intensity (the weight lifted) of their workouts based on their fitness goals. For instance, higher volume with moderate weights can be effective for toning and endurance, while lower volume with heavier weights is suitable for building strength and muscle.
By implementing these strategies for progression and variation, women can optimize their back workouts, continuously improve their strength and performance, and maintain engagement in their fitness routine. This approach not only supports their fitness goals but also helps in building a resilient and healthy back that is less prone to injury.
Expert Advice on Designing Back Workouts for Women
Designing effective back workouts for women requires careful consideration of individual fitness levels, goals, and training preferences. Here's expert advice on crafting back-focused exercise programs tailored for women:
- Assess Individual Needs: Before designing a back workout routine, assess the individual's fitness level, strength, mobility, and any specific goals or limitations. This evaluation helps customize the workout to meet individual needs and maximize results.
- Focus on Compound Movements: Incorporate compound exercises that engage multiple muscle groups in the back, such as rows, pull-ups, and deadlift variations. Compound movements are efficient for building overall strength and muscle mass.
- Emphasize Progressive Overload: Implement progressive overload by gradually increasing the intensity, volume, or resistance of back exercises over time. This progressive approach stimulates muscle growth and adaptation.
- Include Variation and Balance: Ensure variety in back workouts by targeting different areas of the back (upper, middle, lower) with a mix of pulling and rowing exercises. Balance pulling movements (e.g., rows) with stabilizing exercises (e.g., planks) to develop a strong and functional back.
- Prioritize Proper Form and Technique: Focus on mastering proper form and technique to prevent injuries and optimize exercise effectiveness. Emphasize controlled movements and maintain alignment throughout each exercise.
- Customize for Specific Goals: Tailor back workouts based on specific fitness goals, whether it's building strength, improving posture, enhancing athletic performance, or simply maintaining overall fitness. Adjust exercise selection and intensity accordingly.
- Incorporate Recovery Strategies: Allow sufficient rest and recovery between back workouts to promote muscle repair and growth. Adequate sleep, hydration, and nutrition are essential for recovery and overall recovery.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consult with certified fitness trainers, strength coaches, or physical therapists for personalized guidance and programming. They can provide expert advice, correct technique, and modify workouts based on individual progress and feedback.
Conclusion
Back workouts are crucial for women looking to enhance strength, posture, and overall fitness. A strong back not only contributes to a balanced physique but also supports functional movement and daily activities. By focusing on back exercises, women can address muscle imbalances caused by sedentary lifestyles and poor posture, reducing discomfort and the risk of injuries.
Incorporating a variety of back exercises is essential for comprehensive strength development. A balanced routine should include both compound movements like rows and pulldowns, and isolation exercises such as reverse flyes. This variety keeps workouts engaging and stimulates muscle growth.Consistency is key to reaping the rewards of a strong back. A regular routine that includes back exercises at least two to three times a week will aid in progressive strength building. By prioritizing back workouts, women can improve their overall health, posture, and quality of life.