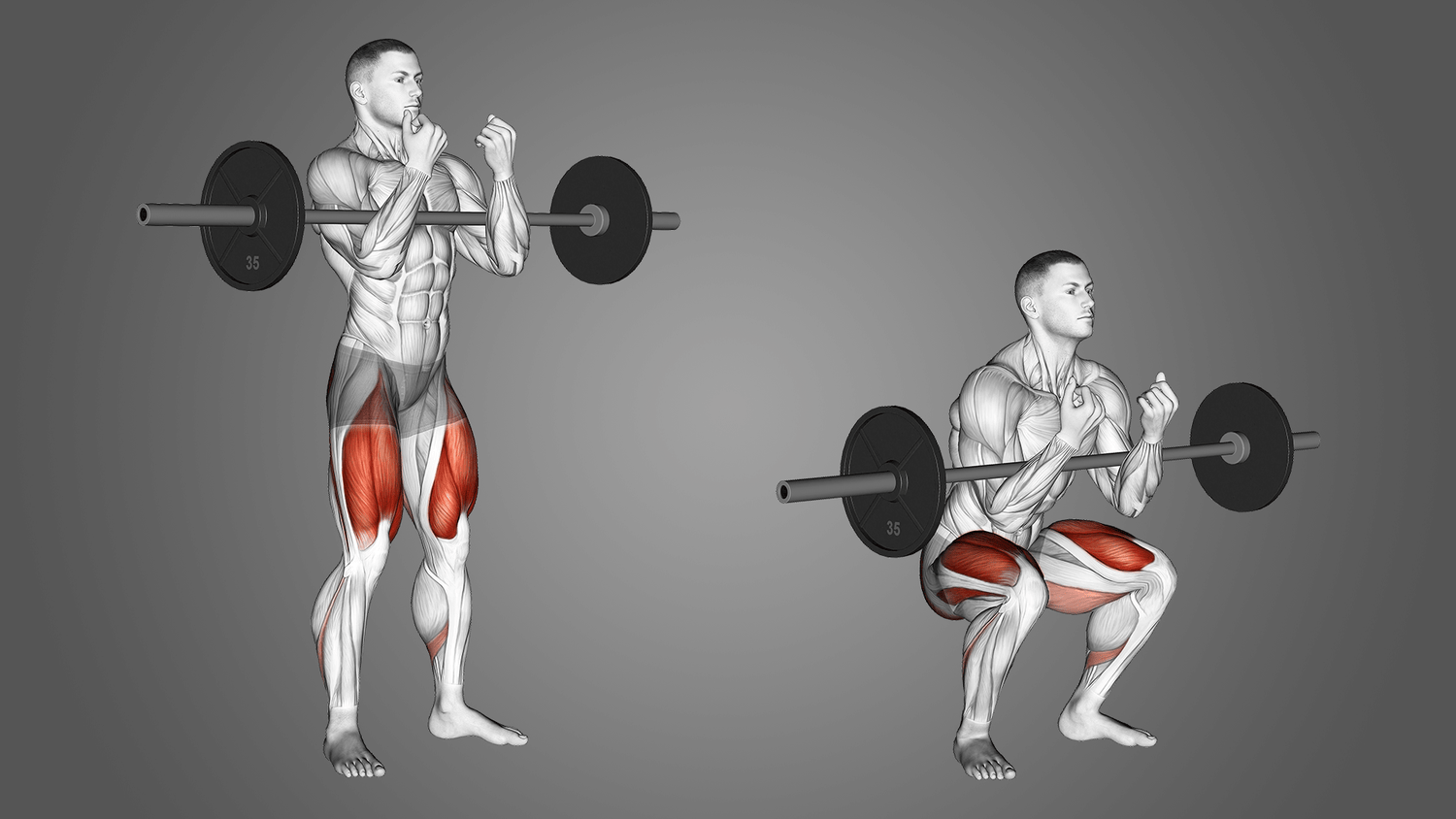
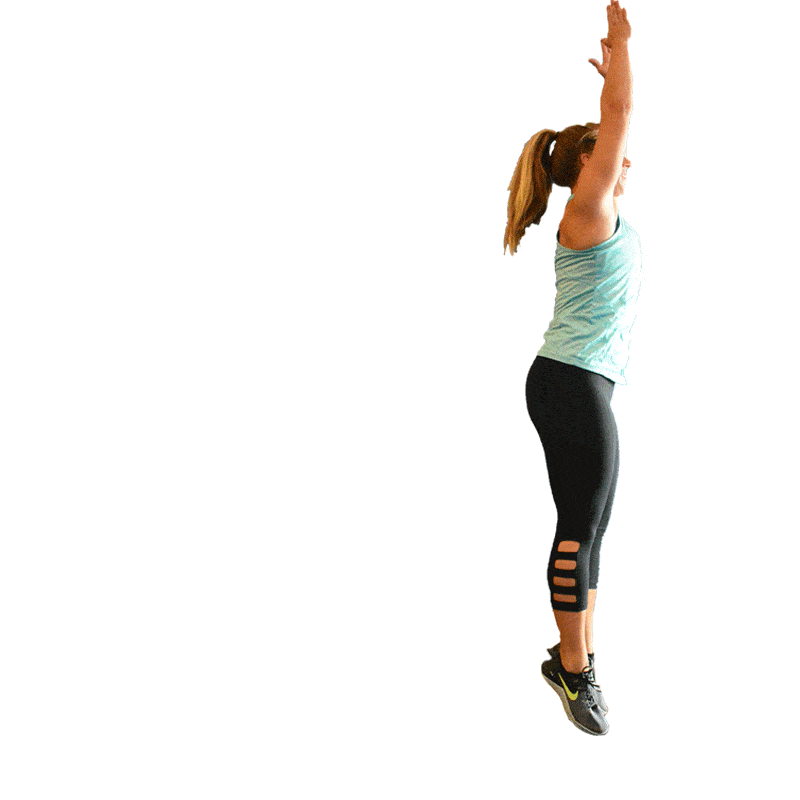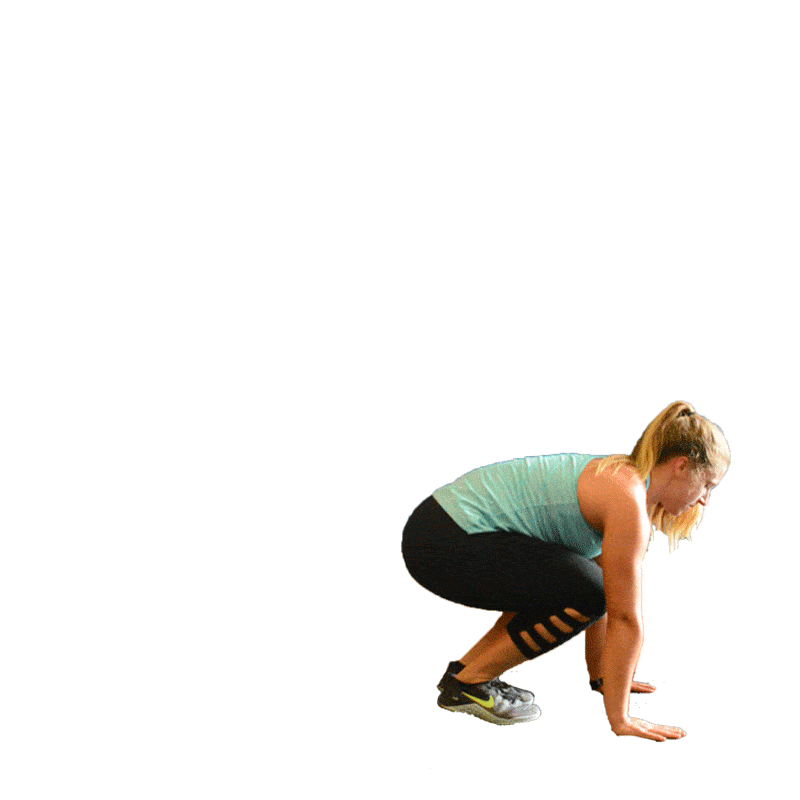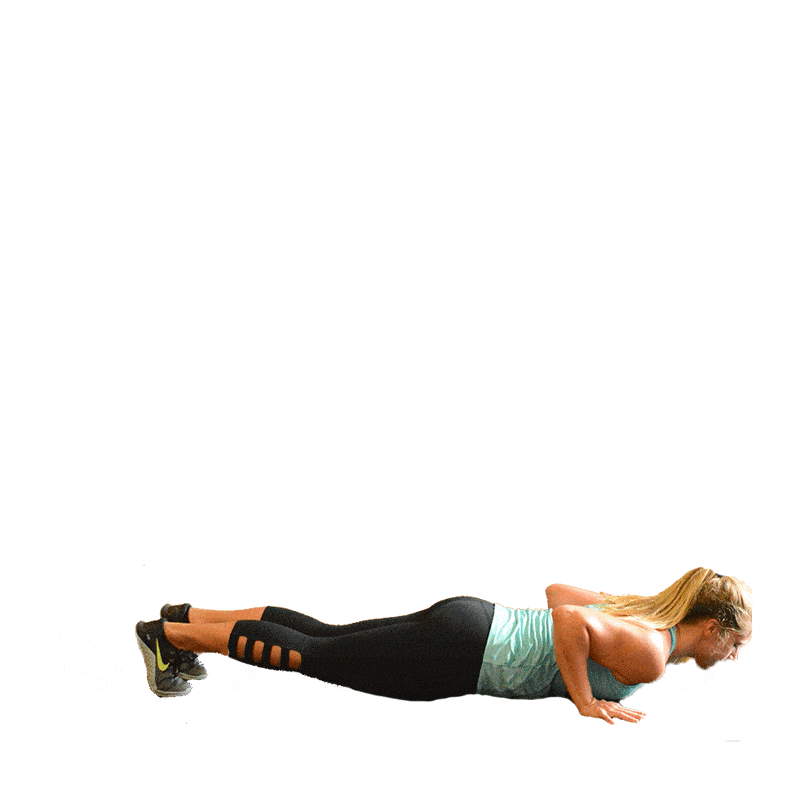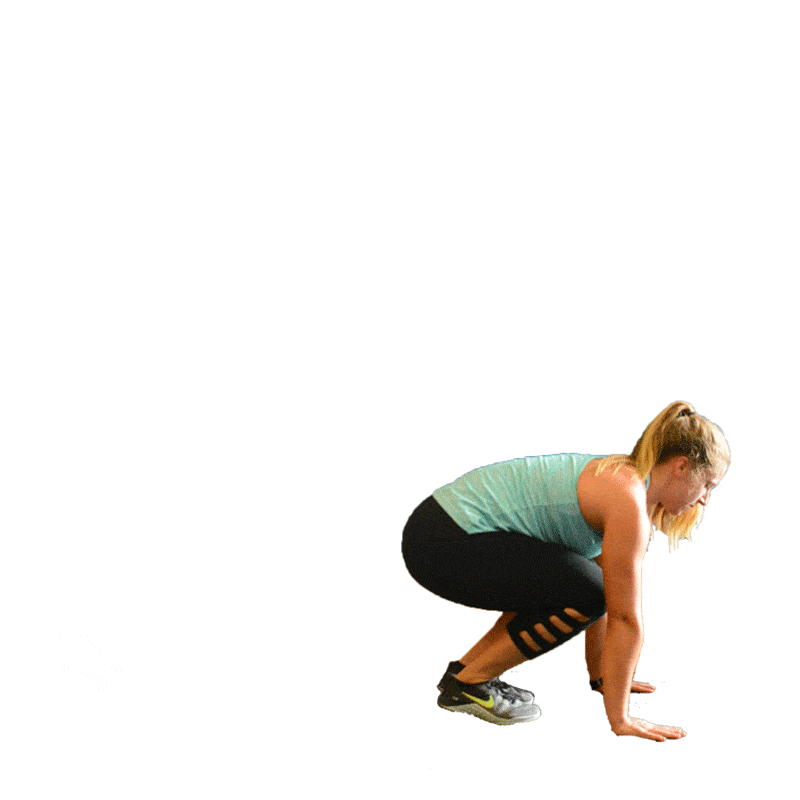The Zercher squat, a unique and dynamic variation of the traditional squat, has gained popularity for its unconventional bar placement and distinctive benefits. Originating from strongman Ed Zercher in the early 20th century, this squat variation places the barbell in the crook of the elbows rather than on the back.
In this introduction, we'll delve deep into the intricate mechanics, astounding benefits, and crucial considerations surrounding Zercher squats. Whether you're a seasoned lifter looking to spice up your routine or a newcomer eager to explore the realm of strength training, this comprehensive guide will equip you with everything you need to know about incorporating this transformative exercise into your regimen.
Zercher Squat Mechanics
Unlike traditional squats, the Zercher squat involves placing the barbell in the bend of the elbows, requiring a unique grip and stance. This variation shifts the load to the front of the body, engaging the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. The biomechanics of the squatting motion in Zercher squats differ from back squats, demanding a more upright torso and increased engagement of the core and upper back muscles. The placement of the barbell in the arms challenges lifters to maintain stability throughout the movement, promoting a holistic approach to strength development.
Zercher Squats or Traditional Squats,which is better?
Comparing Zercher squats with traditional squats reveals key differences and advantages:
|
Aspect |
Zercher Squats |
Traditional Squats |
|
Muscle Engagement |
Places a significant demand on upper back and core muscles |
Distributes the load more evenly across the lower body |
|
Advantages and Disadvantages |
- Increased engagement of upper body |
- Evenly targets lower body muscles |
|
- Improved posture and scapular stability |
- May be preferred for comprehensive lower body development |
|
|
Decision Factors |
Depends on individual fitness goals and preferences |
Considered for a balanced lower |
In summary, the decision to incorporate Zercher squats or traditional squats into a workout routine depends on individual goals, preferences, and specific considerations such as mobility and muscle imbalances. Both variations offer unique benefits, and a well-rounded training program may include a combination of both to ensure holistic muscle development.
Proper Form and Technique
Achieving optimal results with Zercher squats requires precise form and technique. When setting up for Zercher squats, the lifter should place the barbell in the elbows' crook, maintaining a firm grip and lifting it off the ground. The lifter's stance should be shoulder-width apart, with toes slightly turned outward.
As the squat is executed, the lifter should focus on keeping the chest up, ensuring the barbell remains stable in the elbows. The depth of the squat will vary based on individual flexibility and comfort, but the lifter should aim for a range that allows a full range of motion while maintaining proper form.
Muscles Involved
Understanding the muscles engaged during Zercher squats is crucial for tailoring workouts to specific fitness goals. This section provides an in-depth exploration of the primary muscle groups targeted:
Quadriceps
The quadriceps, located at the front of the thigh, play a central role in extending the knee during Zercher squats. As the lifter descends into the squat, the quadriceps contract to support the lowering phase.
Hamstrings
The hamstrings, situated at the back of the thigh, are actively engaged during the upward phase of the Zercher squat. They work in conjunction with the glutes to extend the hip joint.
Glutes
The gluteal muscles, comprising the gluteus maximus, medius, and minimus, are vital for hip extension and stabilisation. Zercher squats target the glutes, contributing to improved strength and aesthetics.
Core Muscles
The Zercher squat places a significant demand on the core muscles, including the rectus abdominis, obliques, and transverse abdominis. These muscles work collectively to stabilise the spine and maintain an upright torso throughout the movement.
Upper Back Muscles
The trapezius, rhomboids, and lats are actively engaged to support the upper back and shoulder region. This engagement contributes to improved posture and scapular stability.
This detailed understanding of muscle involvement enables lifters to customise their Zercher squat routine based on specific muscle development goals.
How to Perform the Zercher Squat
- Begin by setting up the barbell at an appropriate height, typically just below chest level. Position your feet shoulder-width apart for a stable base.
- Adopt an underhand grip, reaching down to grasp the barbell. Lift it to the crooks of your elbows, maintaining a close proximity of your hands.
- Ensure the bar rests comfortably in the elbows with your palms facing up. Your elbows should point forward throughout the exercise.
- Initiate the squat by bending at both the hips and knees simultaneously. Keep your chest up and back straight, aiming for a depth where your thighs are at least parallel to the ground.
- Push through your heels to stand back up, maintaining the barbell in the crooks of your elbows. Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Benefits of Zercher Squats
Zercher squats offer a myriad of benefits, making them a valuable addition to any strength training regimen. The exercise engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously, promoting functional strength applicable to real-life activities. Studies show that Zercher squats activate the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes more intensely than traditional squats, leading to balanced lower body development.Additionally, the unique bar placement emphasises the core and upper back muscles, fostering increased stability and strength in these areas. The Zercher squat's demand for an upright torso also contributes to improved posture, a critical aspect of overall fitness.
Muscle Engagement
The Zercher squat engages a variety of muscle groups, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, upper back, and core. This holistic engagement makes it an efficient compound exercise.
Core Emphasis
Due to the unique placement of the barbell, the Zercher squat places a considerable emphasis on the core muscles. This includes the rectus abdominis, obliques, and deep stabilising muscles.
Upper Back Activation
The upper back muscles, such as the traps and rhomboids, play a crucial role in maintaining an upright posture during the Zercher squat. This can contribute to improved posture and upper back strength.
Quadriceps and Hamstrings
The movement involves flexion and extension of the hips and knees, activating the quadriceps and hamstrings. This balanced engagement promotes overall leg strength.
Glute Activation
The glutes are recruited during the upward phase of the squat, aiding in hip extension. This can be beneficial for individuals looking to strengthen and tone their glute muscles.
Variations of Zercher Squats
Variations in Zercher squats provide versatility in training and address different fitness objectives. This section explores several variations:
Zercher Box Squats
- Incorporating a box into Zercher squats introduces a depth control element.
- The lifter descends until seated on the box, emphasising controlled movement and proper form.
Zercher Lunges
- Adding a lunge component to Zercher squats increases the demand on stabilising muscles and introduces unilateral leg engagement.
- This variation contributes to balanced muscle development and improved coordination.
Zercher Deadlifts
- Combining the Zercher squat with the deadlift movement pattern provides a comprehensive lower body and posterior chain workout.
- This variation challenges the lifter's strength and endurance, promoting overall muscle development.
How to Begin Zerchers?
When starting Zerchers, the first decision to make is whether to lift from the ground or from a rack. Lifting from the ground is more challenging and requires more setup, but it's necessary if you don't have access to a rack. Starting from the ground helps establish leg and elbow spacing early on, preventing issues later. Even with a rack, starting from the floor initially can help find the best positioning.
-
If starting from the floor, arm positioning will likely depend on leg positioning. However, arm positioning is crucial in Zercher squats. Arms too close make balancing difficult, while too far apart may affect back tightness. It might be worth adjusting your deadlift stance to accommodate arm position if necessary.
-
If starting from the rack, especially from the top of a squat, focus on how your elbows interact with your legs at the bottom. Stabbing elbows into quads disrupts the movement. Adjust stance or control descent to avoid this, experimenting with setup to find consistency.
-
Initially, expect discomfort in the elbows. Consider wearing elbow sleeves for protection, gradually adjusting as you get used to the lift. Programming Zerchers varies based on goals. They can range from building upper back and core strength with holds to replacing back squats entirely. Ensure the lift aligns with your training goals to justify its inclusion.
-
Lastly, consider the strain Zerchers place on the lower back and posterior chain. Account for this when integrating them into your routine to prevent overtaxing these areas.
Training Tips and Considerations
Incorporating Zercher squats into a workout routine requires careful consideration and attention to certain training tips:
Starting with Lighter Weights for Beginners
Beginners should initiate Zercher squats with lighter weights to master the form and gradually progress. This approach minimises the risk of injury and allows for a smooth adaptation to the exercise.
Focus on Form
Maintaining proper form is crucial to maximise the benefits and reduce the risk of injury. Ensure your chest stays up, back remains straight, and elbows point forward.
Progressive Overload Strategies
As strength improves, lifters can progressively increase the resistance to induce muscle adaptation. Gradual increments in weight ensure continued challenge and growth.
Integrating Zercher Squats into a Comprehensive Workout Routine: While Zercher squats are effective, a well-rounded workout routine should include a variety of exercises to target different muscle groups. Integrating Zercher squats as part of a comprehensive routine contributes to overall fitness and prevents workout plateaus.
Safety Considerations
- Given the intensity of the Zercher squat, a thorough warm-up is essential. Focus on dynamic stretches and mobility exercises to prepare the muscles and joints.
- Especially for beginners, it's crucial to exercise caution with the amount of weight used. Overestimating your capacity can lead to compromised form and potential injuries.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoiding common mistakes is essential for maximising the effectiveness of Zercher squats and minimising the risk of injury:
Improper Bar Placement
Placing the bar too high or too low in the elbows can compromise form and stability. Ensuring the bar is comfortably nestled in the crook of the elbows maintains control and reduces strain.
Poor Form and Technique
Rushing through Zercher squats with improper form can lead to injuries and diminish the exercise's benefits. Focusing on controlled, deliberate movements ensures optimal muscle engagement and reduces the risk of strain.
Overloading Without Mastering the Basics
Attempting heavy weights before mastering the fundamental Zercher squat technique increases the risk of injury. Building a solid foundation with lighter weights establishes proper movement patterns before progressing to heavier loads.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Zercher squat stands as a versatile and effective exercise that offers unique advantages in muscle engagement and functional strength. From its distinct mechanics to the targeted muscles involved, the Zercher squat provides lifters with an opportunity to enhance their lower body strength, core stability, and overall fitness. By understanding proper form, training tips, and variations, individuals can integrate Zercher squats into their workout routines responsibly. The exercise's real-life applications and success stories further underscore its transformative potential, making it a valuable addition to any strength training regimen.